Describe how cigarette smoke is responsible for the development of lung cancer:
The carcinogenic chemical (especially tar) cause the cell to stop responding to cell signals and to stop responding to normal cell mechanisms (i.e. apoptosis). This means that the cell divides uncontrollably forming a tumour, this tumour can become cancerous if a mutation of the proto-oncogen genes to oncogen genes occur during cell division.
Tuesday, 18 February 2014
Monday, 17 February 2014
Cell and Nuclear Division
Cell division that results in a daughter cell with a complete set of identical instructions is called mitosis.
What is mitosis important for?
What is mitosis important for?
- Production of genetically identical cells
- Growth (Replacement of cells)
- Repair of tissues
- Asexual reproduction
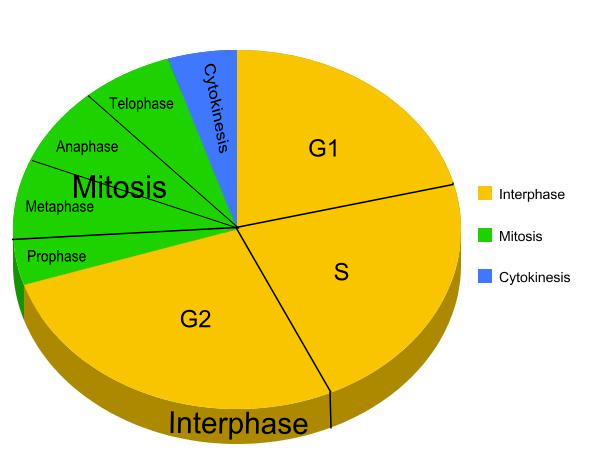
Cell cycle

During S phase DNA replicates:
- Original DNA splits into 2 strands breaking H-bonds
- Nucleotides join up to the template strand
- Pair up according to the complementary base pair rules (H-bonds reform)
- 2 new, identical helices formed
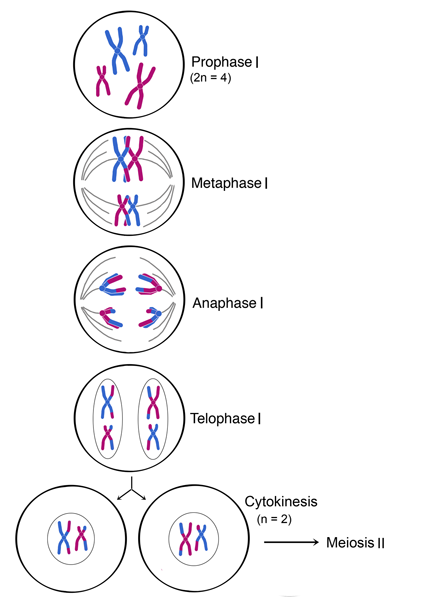
Prophase:
(Centriole replicates before prophase)
- Chromosomes coil up becoming shorter and thicker
- Nuclear envelope breaks into vesicles
- Nucleolus forms parts of chromosomes
- Centrioles move to opposite poles and form spindles
Metaphase:
- Each centriole reaches a pole
- Centrioles organise production of spindle microtubules
- Chromosomes line up attached by the centromere along the equator of the spindle
Anaphase:
- Chromatids move to opposite poles, centromeres first, pulled by the microtubules
Telophase:
- Nuclear envelope and nucleolus reform
- Chromatids uncoil to form chromatin
- Beginning of cytokinesis
- Centriole will replicate during interphase before the next nuclear division
Cytokinesis= the division of the cytoplasm and cell into two by constriction from the edges of the cell
Chromosome=A structure formed from DNA that condenses in a nucleus before mitosis can occur
Chromatin= Material containing DNA and proteins
Sister Chromatid= An arm of a chromosome. These are joined by a centromere and are separated and pulled to opposite poles
Centromere= A structure which allows chromosomes to be attached to spindle fibres at the equator
Spindle fibres= Fibres formed from the centrioles at opposite ends of the poles which chromosomes are pulled along
Equator= The metaphase plate where chromosomes align, attach to spindle fibres and sister chromatids are separated. A cleavage furrow or cell plate is formed here during cytokinesis
Centriole= Replicate and are located at opposite poles of the cell. Spindle fibres form from these
Base pair rules= Rules stating which nucleotide bases join together. Crucial during DNA replication in interphase. C=G, A=T
Cell membranes and transport
- Steepness of the concentration gradient
- Temperature
- Surface Area
- Distance/Thickness of membrane
- Size of molecule
Facilitated diffusion= Diffusion with the help of protein molecules (transports water and glucose
Osmosis= The net movement of water from a region of high to low water potential through a partially permeable membrane. (Pure water has a water potential of 0 any addition of solute lowers)
Active transport= Uses ATP to move substances against their concentration gradient, (conducted by carrier proteins)
Endocytosis= A section of the plasma membrane surrounds a large object and then "pinches" off to form a vesicle (Bulk transfer of materials into the cell)
Exocytosis= Transported substances are carried in vesicles to the cell membrane where they are released after fusion with the plasma membrane
The effect of water potential on cells
Animal:
Plant:
Enzymes
Defintion= Enzymes are globular proteins that catalyse metabolic reactions
Basics:
Lock and key method= Active site has identical shape to substrate (complementary)
Induced fit= due to interactions between R-groups
Catalyst=lowers the activation energy by providing an alternative pathway
Activation energy= the energy that must be put into a chemical system in order for the reaction to occur
Denaturing due to temperature:
- Increased temp.=Increased kinetic energy= Substrate and enzymes collide more= increased ESC formed
- Too much kinetic energy means that bonds holding tertiary structure together break
Denaturing due to pH:
(pH is the measure of H+ ion concentration)
- Enzymes have an optimum pH
- Outside the optimum pH H+ ions interact with R-groups on amino acids
- Breaks ionic bond (tertiary structure broken)
- Active site is permanently altered
Inhibitors:
- Are chemicals which reduce the rate of enzyme controlled reactions
- They combine with the active site so that it can no longer bind to the substrate
- The degree of inhibition increases with the concentration of the inhibitor
Non-competitive:
- Auosteric binding site
- Causes conformational change to the active site
- Alters shape of active site
- Tend to be permanent binding
- Altering the concentration of substrate has no effect as inhibitor is not binding to the active site
- Stops enzyme binding directly as the inhibitor molecule is similar to the substrate
- Binds directly to the active site
- Not permanent
- Increasing the substrate concentration reduces the effect of the inhibitor
Measuring the course of a reaction:
(The rate of enzyme controlled reactions can be measured in two ways)
1. Measure the rate of product formation
E.g 2H2O2---->2H2O+O2 (measure the amount of gas produced)
2. Measuring the rate of substrate breakdown
E.g Starch----->Maltose (Take a drop of solution every minute-iodine solution)
Comparing rates of reaction:
Reaction=Different concentrations of catalase to the same volume of substrate
Problems=All lines eventually meet and measuring total volume of oxygen produced does not allow you to compare the rates of reaction
Solution= Therefore the initial rate of reaction is measured instead
Why do enzymes speed up reactions?
More enzymes present the more active sites there will be for the substrate to bind to. (As long as there is plenty of substrate available)
The effect of substrate concentration
As substrate concentration increases, the initial rate of reaction also increases (the more substrate molecules there are around the more often an enzyme's active site can bind with one). There is a point where every enzyme active site is working continuously. The enzyme is working at its maximum possible rate known as Vmax.
Calculating the initial rate of reaction:
Draw a tangent to the graph as close to 0 as possible
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)