What is mitosis important for?
- Production of genetically identical cells
- Growth (Replacement of cells)
- Repair of tissues
- Asexual reproduction
Cell cycle
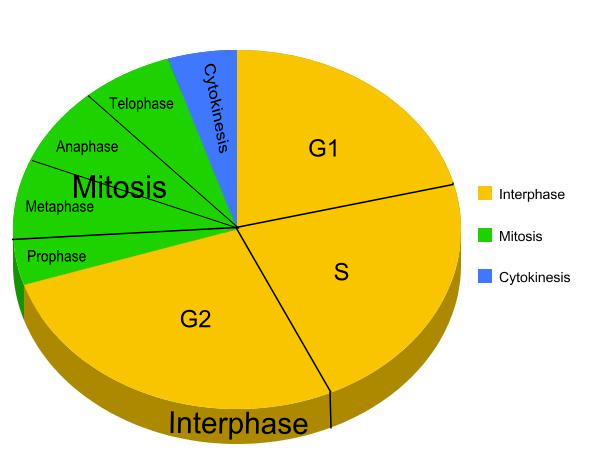
During S phase DNA replicates:
- Original DNA splits into 2 strands breaking H-bonds
- Nucleotides join up to the template strand
- Pair up according to the complementary base pair rules (H-bonds reform)
- 2 new, identical helices formed
Prophase:
(Centriole replicates before prophase)
- Chromosomes coil up becoming shorter and thicker
- Nuclear envelope breaks into vesicles
- Nucleolus forms parts of chromosomes
- Centrioles move to opposite poles and form spindles
Metaphase:
- Each centriole reaches a pole
- Centrioles organise production of spindle microtubules
- Chromosomes line up attached by the centromere along the equator of the spindle
Anaphase:
- Chromatids move to opposite poles, centromeres first, pulled by the microtubules
Telophase:
- Nuclear envelope and nucleolus reform
- Chromatids uncoil to form chromatin
- Beginning of cytokinesis
- Centriole will replicate during interphase before the next nuclear division
Cytokinesis= the division of the cytoplasm and cell into two by constriction from the edges of the cell
Chromosome=A structure formed from DNA that condenses in a nucleus before mitosis can occur
Chromatin= Material containing DNA and proteins
Sister Chromatid= An arm of a chromosome. These are joined by a centromere and are separated and pulled to opposite poles
Centromere= A structure which allows chromosomes to be attached to spindle fibres at the equator
Spindle fibres= Fibres formed from the centrioles at opposite ends of the poles which chromosomes are pulled along
Equator= The metaphase plate where chromosomes align, attach to spindle fibres and sister chromatids are separated. A cleavage furrow or cell plate is formed here during cytokinesis
Centriole= Replicate and are located at opposite poles of the cell. Spindle fibres form from these
Base pair rules= Rules stating which nucleotide bases join together. Crucial during DNA replication in interphase. C=G, A=T
No comments:
Post a Comment